算法入门1:堆栈和队列互相模拟
堆栈模拟队列
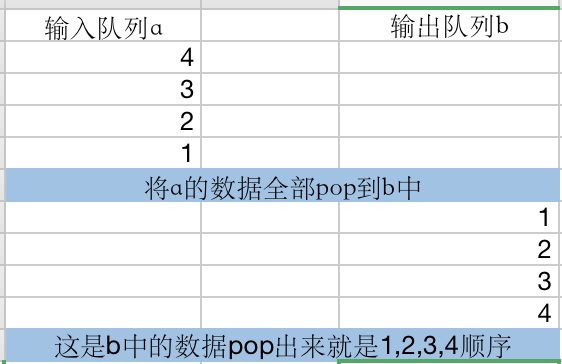
需要两个堆栈, 一个负责输入, 另一个负责输出
- 将数据push到输入队列a中
- 将a中数据pop到输出队列b中
- pop出b中数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| public static void stackToQueue(Stack<Integer> inPut){
Stack<Integer> outPut = new Stack<>();
while (!inPut.isEmpty()){
outPut.push(inPut.pop());
}
while (!outPut.isEmpty()){
System.out.println(outPut.pop());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
stack.push(5);
stackToQueue(stack);
}
|
队列模拟堆栈
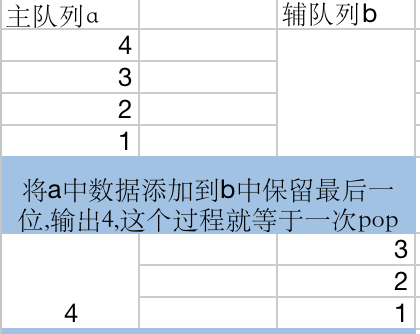
需要一个堆栈作为辅助列
- 将数据push到主队列a中
- 将a中数据添加到b中保留最后一位,输出4,这个过程就等于一次pop
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> master = new LinkedList<Integer>();
master.add(1);
master.add(2);
master.add(3);
master.add(4);
master.add(5);
popAll(master);
}
private static void popAll(Queue<Integer> master) {
Queue<Integer> help = new LinkedList<Integer>();
while (master.size() > 1) {
help.add(master.poll());
}
System.out.println(master.poll());
if (!help.isEmpty()){
popAll(help);
}
}
|

